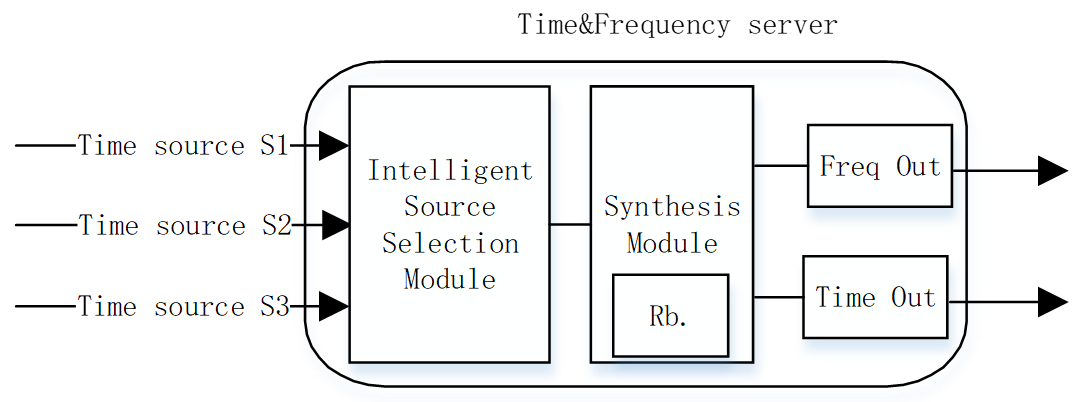
Since the release of the IEEE1588v2 (PTP) timing technology standard in 2008, PTP timing technology has been widely used around the world due to its convenience and high accuracy (relative to NTP), and now PTP timing technology is used as a high-precision long-distance time synchronization method by various industries such as Telecom Operator, Power Grid, and railway and subway communication networks.PTP timing technology realizes timing through the two-way message exchange in the figure below.
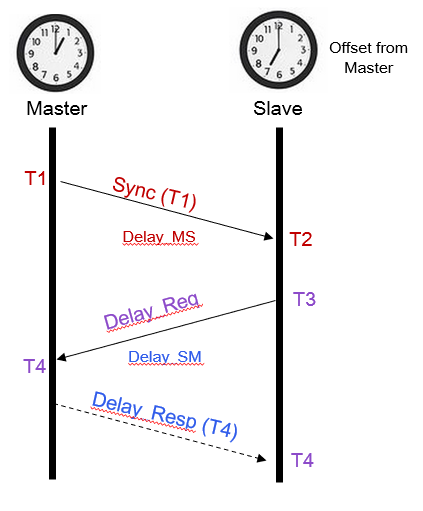
T1–The timestamp when the sync message departs from the master;
T2–The timestamp when sync message arrives at the slave;
T3– The timestamp when the delay request message departs from the slave
T4–The timestamp when delay response message arrives at the master;
Dms- master to slave channel delay;
Dsm- slave to master channel delay;
Offset- The time difference between slave and master device.
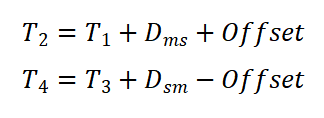
Symmetrical case:
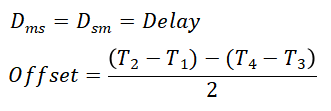
Asymmetrical case:
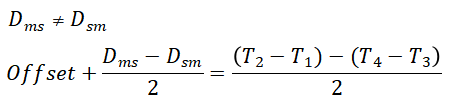
From the above principle, it can be found that the current PTP timing technology can only calculate the time error by assuming that the go and back delay is equal, but this is not in line with the actual situation. The difference in the length of the round-trip optical cable of the transmission link and the difference in the uplink processing speed of the intermediate device will lead to unequal round-trip transmission delay (also known as asymmetric delay), and these errors will generally be added to the synchronization error of the slave device, that is, asymmetric delay Asym=(Dms-Dsm)/2.
In order to eliminate the asymmetric delay of PTP as much as possible, engineers in the industry have used various methods to minimize the impact of asymmetric delay for many years. For example, use optical fiber transmission instead of electric cable transmission, try to use FPGA or other dedicated hardware circuits for timestamps as close to the physical layer as possible, and try to use bidirectional fiber transmission to avoid asymmetric delays caused by unequal distances between round-trip optical paths. But even so, the two channels going back and forth in the same optical fiber will cause asymmetric time delays due to the dispersion effect of light. Assuming that 1490nm is used as the outbound channel and 1550nm is used as the return channel. In a typical G.652 optical fiber, it is estimated that the asynchronous delay brought by 100km optical fiber is 50ns. For 5G time synchronization networks that pursue sub-nanosecond or even picosecond levels, this error is unacceptable.
In response to this key flaw that has restricted the development of PTP for many years, Taifu invented a method that can automatically measure the asymmetric delay of PTP in a single-fiber bidirectional environment and automatically compensate. The PTP synchronization mechanism implemented by this method can automatically eliminate the asymmetric delay caused by the fiber dispersion effect and improve the accuracy of PTP time synchronization.
The PTP function of TFT3001 device integrates a patented technology on the basis of the G.8275.1 standard, which can accurately calculate and automatically compensate for the asynchronous delay caused by optical fiber dispersion, and truly achieve the master-slave clock synchronization deviation of ≤5ns, and the synchronization resolution ≤ 1ns.

If you have any questions, please feel free to consult via email or phone.
Email: liyan@groundbeidou.com
Phone: +86 15928828658